The volt-ampere characteristic is the relationship between the voltage u applied to both ends of the diode and the current flowing through the = diode, i.e., I=f (u).Volts of 2CP12 (ordinary silicon = diode) and 2AP9 (ordinary germanium diode).
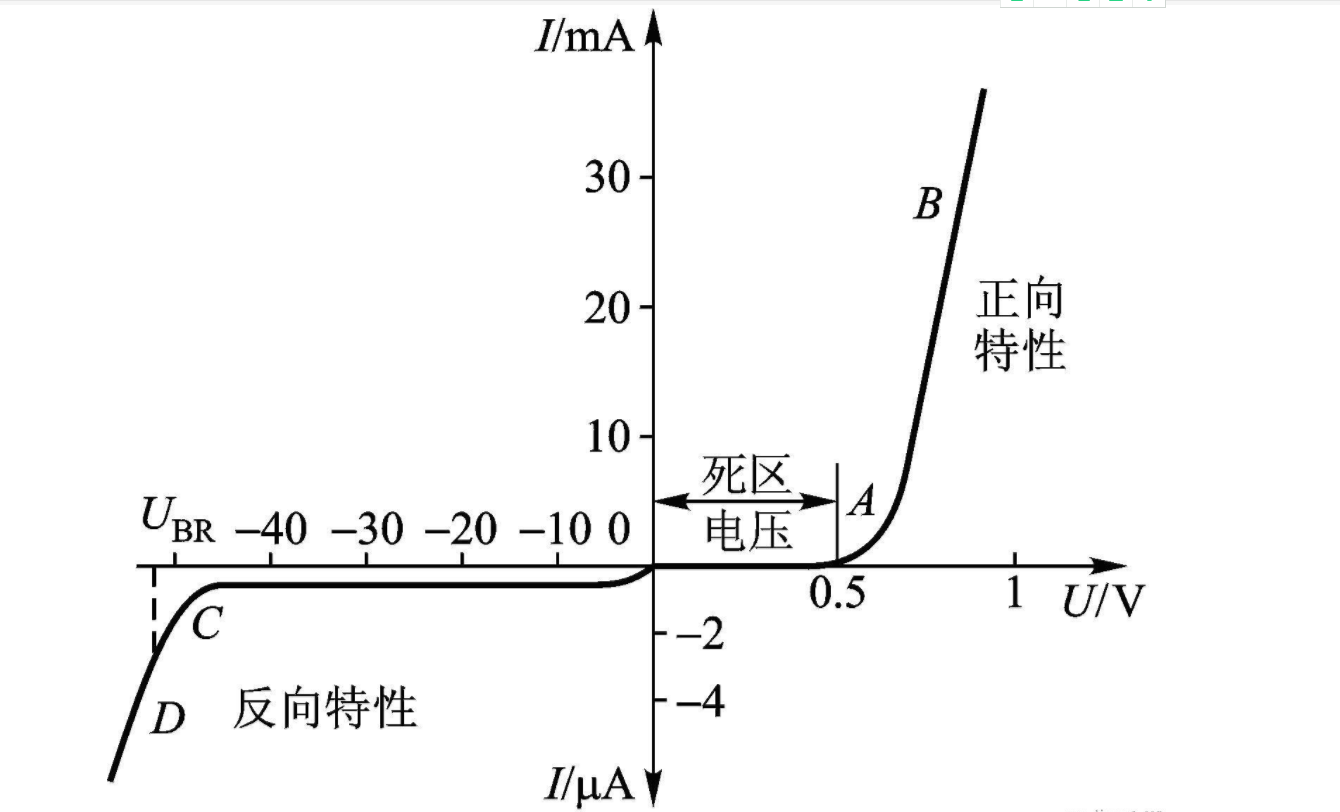
(1) positive characteristics
The first quadrant of the diode volt - false characteristic curve is called forward characteristic.In the initial part of the forward characteristic, because the forward voltage is small, the external electric field is not enough to overcome the blocking effect of the internal electric field on most carriers, and the forward current is almost zero. This region is called the volt-ampere characteristic curve of the forward diode
Dead zone, the corresponding voltage is called dead zone voltage.The dead zone voltage of silicon tube is about 0.5V, and that of germanium tube is about 0.2 V.
When the forward voltage exceeds a certain value, the internal electric field is greatly weakened, the forward current rapidly increases, diode conduction, this area is called the positive guide pass area.Diode a positive guide through, as long as there is a slight change in the forward voltage, the forward current will change greatly, the forward characteristic curve of the diode is very steep.Therefore, when the diode is passed through through a positive guide, the forward pressure drop on the tube is not large and the change of the forward pressure drop is small. Generally, the silicon tube is about o. 7V and the germanium tube is about 0. 3V.Therefore, when using the diode, if the applied voltage is large, generally in the circuit to connect the current limiting resistance, so as not to produce too much current to burn out the diode.
(2) reverse characteristics
The third quadrant of the diode voltages characteristic curve is called the reverse characteristic.Within a certain range of reverse voltage, the reverse current is very small and does not change much, which is called the reverse cut-off region.This is because the reverse current is formed by the drift motion of a few carriers;Under a certain temperature, the number of little particles is basically unchanged, so the reverse current is basically constant, and the size of the reverse voltage has nothing to do with it, so it is usually called the reverse saturation current.
(3) reverse breakdown characteristics
When the reverse voltage continues to increase to a certain value, the reverse current in the diode will suddenly increase, and we say that the diode has a reverse breakdown. The characteristics of this section are shown in section D of 1.2.6.Reverse breakdown occurs p-n junction has a lot of reverse current, serious when will lead to damage of p-n junction, so common diode should avoid the breakdown, but must I make a zener diode tube in breakdown state, because of the larger changes in the breakdown area while the current and voltage can keep basically remain unchanged, use this feature, voltage regulator tube can have the effect of voltage regulation.

 Inglês
Inglês  Chinês
Chinês  Alemão
Alemão  Coreano
Coreano  Japonês
Japonês  Farsi
Farsi  Portuguese
Portuguese  Russian
Russian  Espanhol
Espanhol 





